- No. 268 Xianghe Street, Economic Development Zone of Xingtai city, Hebei 054001 China
- Byron@hbhongri.cn
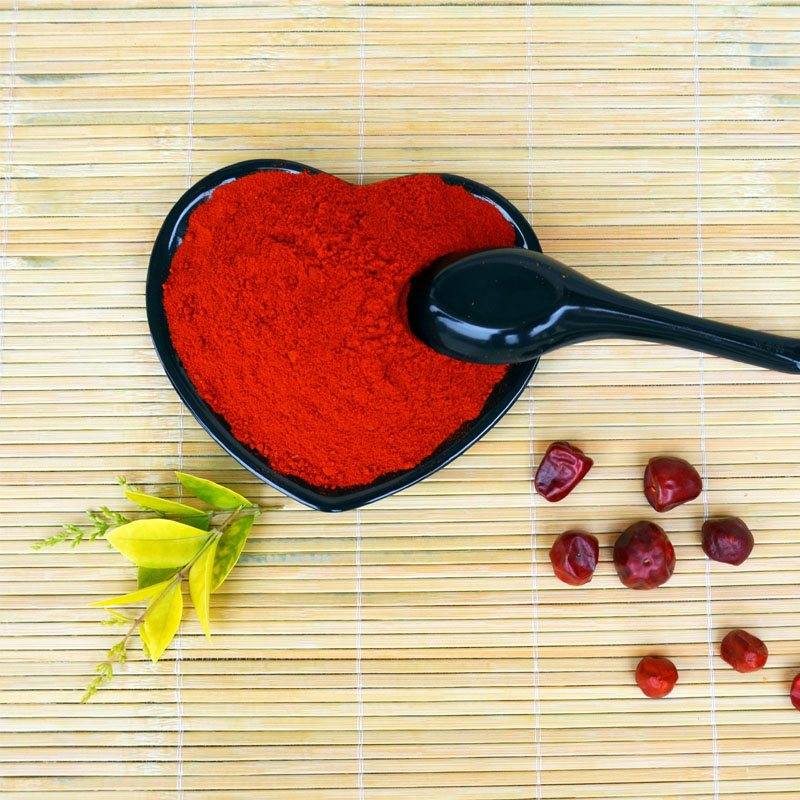
capsicum annuum paprika
Exploring Capsicum Annuum The Versatile Paprika
Capsicum annuum, commonly known as paprika, is a vibrant and flavorful spice derived from the dried fruits of various Capsicum pepper species. This plant is a member of the Solanaceae family, which includes other well-known vegetables such as tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplants. Paprika is renowned not only for its culinary uses but also for its diverse nutritional benefits and cultural significance across the globe.
Historical Background
Paprika's story begins in South America, where it was first cultivated by indigenous peoples thousands of years ago. It made its way to Europe in the 16th century, likely brought back by explorers who returned from their voyages. Hungary and Spain quickly became the main producers of this spice, leading to a rich tradition of paprika cultivation and consumption. In Hungary, paprika has been elevated to the status of a national spice, playing a vital role in the country’s signature dishes, such as goulash and pörkölt. Spanish paprika, on the other hand, is known for its distinct smokiness, thanks to the drying method over an oak fire, contributing to various traditional dishes like chorizo.
Varieties of Paprika
There are numerous varieties of paprika, each with its unique flavor profile, color, and heat level. The most common types include sweet paprika, hot paprika, and smoked paprika. Sweet paprika is mild and slightly sweet, making it a versatile spice for seasoning various dishes without overwhelming the palate. Hot paprika is spicier and adds a kick to meals, while smoked paprika imparts a deep, smoky flavor that enhances everything from stews to grilled meats. These varieties allow chefs and home cooks to tailor their dishes to achieve the desired taste and heat level.
Culinary Uses
capsicum annuum paprika

Paprika is incredibly versatile, often used in different cuisines worldwide. Its brilliant red color makes it an attractive garnish on dishes like deviled eggs or potato salads, while its flavor enhances sauces, soups, and stews. In Mediterranean cooking, paprika is essential in spice blends like pimentón and harissa, adding depth and complexity to the flavor profile. In addition, the spice is prominent in Eastern European dishes, where it is essential in creating hearty, warming meals.
Nutritional Benefits
Beyond its culinary uses, paprika also boasts several nutritional benefits. It is rich in antioxidants, particularly carotenoids, which help protect the body against oxidative stress. Additionally, paprika contains vitamins A, C, and E, contributing to overall health by supporting immune function, promoting healthy skin, and improving vision. The spice may also possess anti-inflammatory properties and is believed to aid digestion.
Cultural Significance
Paprika is not just a spice; it is a cultural emblem in many regions. In Hungary, the annual Paprika Festival celebrates the harvest and the significance of paprika in local cuisine. It features various dishes, cooking competitions, and cultural performances, highlighting the importance of this spice in Hungarian identity. Similarly, in Spain, the cultivation and use of paprika play a key role in the culinary heritage of regions like La Vera.
Conclusion
In summary, Capsicum annuum, or paprika, is much more than just a simple spice. It carries with it a rich history, a myriad of flavors, and numerous health benefits. As a staple ingredient in many kitchens around the world, paprika continues to inspire chefs and food enthusiasts alike. Whether sprinkled atop a dish for color or used as a key ingredient in a recipe, paprika remains a beloved and essential spice in global cuisine, celebrating both its versatility and cultural importance.
-
Turmeric Rhizome Powder: A Golden Treasure from Roots to TableNewsJul.28,2025
-
The Versatile Application Of Crushed Red Hot Peppers: Lighting Up The Red Flames On The Dining TableNewsJul.28,2025
-
The Paprika: A Touch Of Vibrant Red In Color, Flavor, And CultureNewsJul.28,2025
-
Ground Turmeric: A Modern Examination of an Ancient SpiceNewsJul.28,2025
-
Capsicum Liquid Extract: Features, Applications, and ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
Application of Capsicum Liquid Extract in FoodNewsJul.28,2025