- No. 268 Xianghe Street, Economic Development Zone of Xingtai city, Hebei 054001 China
- Byron@hbhongri.cn
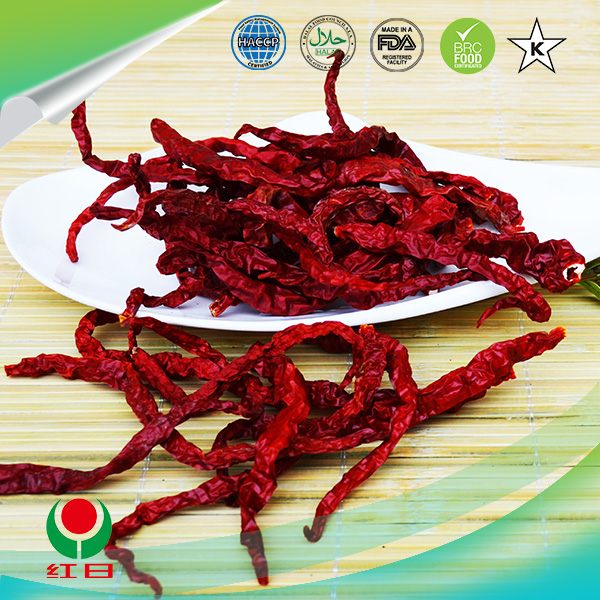
dried hot chili peppers
The Versatile World of Dried Hot Chili Peppers
Dried hot chili peppers have been a staple in cuisines around the world for centuries. They are not merely a way to add heat; they bring depth of flavor, color, and even nutritional benefits to dishes. From the fiery heat of a ghost pepper to the smoky flavor of chipotle, dried chili peppers offer a wide array of tastes and levels of spiciness that can cater to any palate.
Historical Significance
Chili peppers originated in Central and South America and were integral to the diets of indigenous peoples long before the arrival of European settlers. When the Spanish and Portuguese explored the Americas, they discovered these vibrant peppers and brought them back to Europe, Asia, and Africa. Over time, these peppers adapted to local climates and culinary traditions, leading to the creation of unique varieties across different cultures. Today, dried hot chili peppers are celebrated in traditional dishes from Indian curries to Mexican salsas and Thai stir-fries.
Varieties and Flavor Profiles
Dried hot chili peppers come in an astonishing range of varieties, each with its own distinct flavor profile and heat level. For instance, the Serrano pepper, known for its bright, grassy flavor, has a heat level that ranges from 2,500 to 5,000 Scoville Heat Units (SHU). In contrast, the Habanero pepper, with its fruity notes and intense heat (between 100,000 to 350,000 SHU), is often used in sauces and marinades for those who can handle the heat.
One of the most versatile dried chilies is the Ancho pepper, which is the dried version of the Poblano pepper. With a rich, sweet flavor and a moderate heat level (1,000 to 2,000 SHU), Anchos are often ground into powders to enhance mole sauces or used whole in stews. Chipotle peppers, which are smoked Jalapeños, add a unique smoky flavor and moderate heat (about 2,500 to 8,000 SHU) to a variety of dishes, making them a favorite among barbecue enthusiasts.
Culinary Applications
dried hot chili peppers
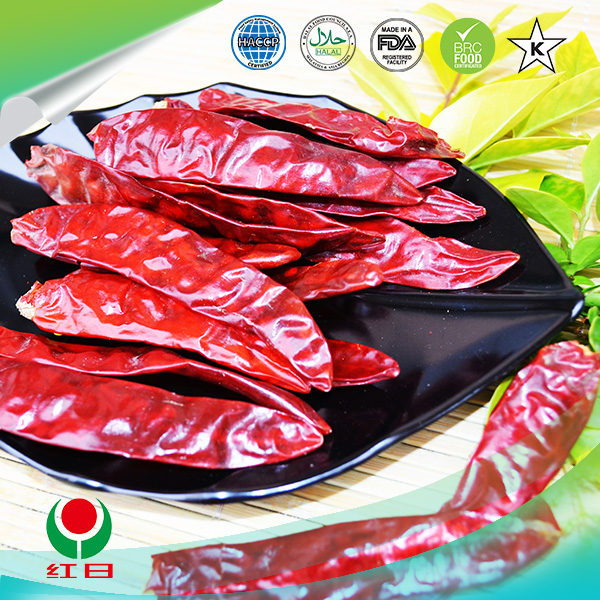

Incorporating dried hot chili peppers into cooking can elevate a dish from ordinary to extraordinary. One of the simplest ways to use them is by rehydrating the dried peppers. By soaking them in hot water for 20 to 30 minutes, they become pliable and can be blended into sauces, pastes, or marinades.
Dried chili powders and flakes can also be sprinkled into soups, stews, and stir-fries to add an instant kick. For those who enjoy experimenting, creating a homemade chili powder blend by mixing various dried peppers can yield unique flavors tailored to personal preferences.
Additionally, many cultures utilize dried chili peppers to create spice blends. In India, for example, dried chilis are ground into powdered masalas, while in Mexico, combinations of dried chilies are essential in making traditional sauces like mole and salsas.
Nutritional Benefits
Beyond their culinary uses, dried hot chili peppers also offer several health benefits. They are rich in vitamins A, C, and E, antioxidants, and capsaicin, the compound responsible for the heat. Capsaicin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, aid in digestion, and even help in weight management by boosting metabolism.
Conclusion
Dried hot chili peppers are far more than just a spicy ingredient; they are a bridge between history, culture, and innovative culinary practices. With their diverse flavors and potential health benefits, they invite chefs and home cooks alike to explore the vibrant world of spice. Whether you’re aiming to create a fiery dish or simply wishing to enhance the flavor of your meal, dried hot chili peppers are the perfect ingredient to unleash your culinary creativity.
-
Turmeric Rhizome Powder: A Golden Treasure from Roots to TableNewsJul.28,2025
-
The Versatile Application Of Crushed Red Hot Peppers: Lighting Up The Red Flames On The Dining TableNewsJul.28,2025
-
The Paprika: A Touch Of Vibrant Red In Color, Flavor, And CultureNewsJul.28,2025
-
Ground Turmeric: A Modern Examination of an Ancient SpiceNewsJul.28,2025
-
Capsicum Liquid Extract: Features, Applications, and ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
Application of Capsicum Liquid Extract in FoodNewsJul.28,2025