- No. 268 Xianghe Street, Economic Development Zone of Xingtai city, Hebei 054001 China
- Byron@hbhongri.cn
fermenting dried chili peppers
The Art of Fermenting Dried Chili Peppers
Fermenting dried chili peppers is an ancient culinary practice that brings out unique flavors and health benefits. This technique not only preserves the peppers but also enhances their taste, making them a delightful addition to various dishes. In this article, we will explore the process of fermenting dried chili peppers, the benefits of fermentation, and some delicious ways to use them in your cooking.
The journey of fermenting dried chili peppers begins with selecting the right variety. Many types of chili peppers can be used, but some popular choices include arbol, guajillo, and cayenne. These varieties possess rich flavors and varying heat levels, allowing for a range of fermentation outcomes. Once you’ve chosen your peppers, the first step is to hydrate them. Soak the dried chilis in warm water for about 30 minutes until they become pliable. This rehydration process is crucial as it allows the peppers to break down during fermentation, releasing their natural flavors.
After hydration, it’s essential to prepare the peppers for fermentation. Remove the stems and seeds if desired, as this will reduce the heat and create a smoother texture. You can mash or blend the peppers with some of the soaking liquid to create a paste. This paste will be the base of your ferment. Next, it’s time to mix in salt, which acts as a preserving agent while promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. The general rule of thumb is to use about 2-3% salt based on the weight of the peppers.
fermenting dried chili peppers
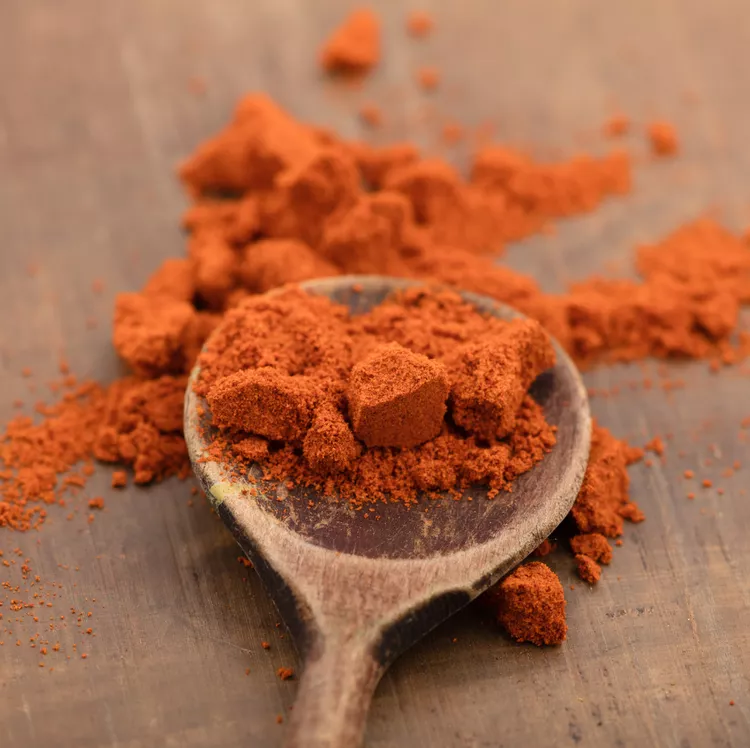

The fermentation process requires a suitable environment. Transfer the pepper paste into a clean glass jar, leaving some headspace at the top. A fermentation weight or a clean piece of plastic wrap can help keep the paste submerged under the brine, preventing mold formation. Seal the jar loosely to allow gases to escape during fermentation. Place the jar in a cool, dark place, ideally around 60-70°F (15-21°C), and let it ferment for 1-3 weeks. The duration depends on your taste preference; longer fermentation will yield a tangier flavor.
As the peppers ferment, you'll notice changes in aroma and color. The beneficial bacteria are at work, breaking down sugars and creating lactic acid, which contributes to the tangy flavor profile. After the desired fermentation period, your chili paste can be stored in the refrigerator to slow the process. It can last for several months, allowing you to enjoy the fruits of your labor well into the future.
Fermented dried chili peppers can be used in various culinary applications. They make an excellent base for hot sauces, adding depth and complexity to your favorite recipes. You can also incorporate them into marinades, dressings, or stews, lending a unique, fermented kick. Additionally, use them as a spicy condiment to elevate sandwiches, tacos, or grilled meats.
In summary, fermenting dried chili peppers not only preserves this flavorful ingredient but also elevates it to new culinary heights. By following the simple steps of hydration, mixing with salt, and allowing nature to take its course, you can create a versatile and delicious condiment that enhances your cooking. Whether you're a cooking enthusiast or a curious beginner, this fermentation journey is sure to add excitement and flavor to your kitchen adventures. So grab those dried chili peppers and start experimenting today!
-
Turmeric Rhizome Powder: A Golden Treasure from Roots to TableNewsJul.28,2025
-
The Versatile Application Of Crushed Red Hot Peppers: Lighting Up The Red Flames On The Dining TableNewsJul.28,2025
-
The Paprika: A Touch Of Vibrant Red In Color, Flavor, And CultureNewsJul.28,2025
-
Ground Turmeric: A Modern Examination of an Ancient SpiceNewsJul.28,2025
-
Capsicum Liquid Extract: Features, Applications, and ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
Application of Capsicum Liquid Extract in FoodNewsJul.28,2025