- No. 268 Xianghe Street, Economic Development Zone of Xingtai city, Hebei 054001 China
- Byron@hbhongri.cn
Exploring the Benefits of Turmeric and Curcumin Powder for Health and Wellness
The Golden Power of Turmeric and Curcumin Powder
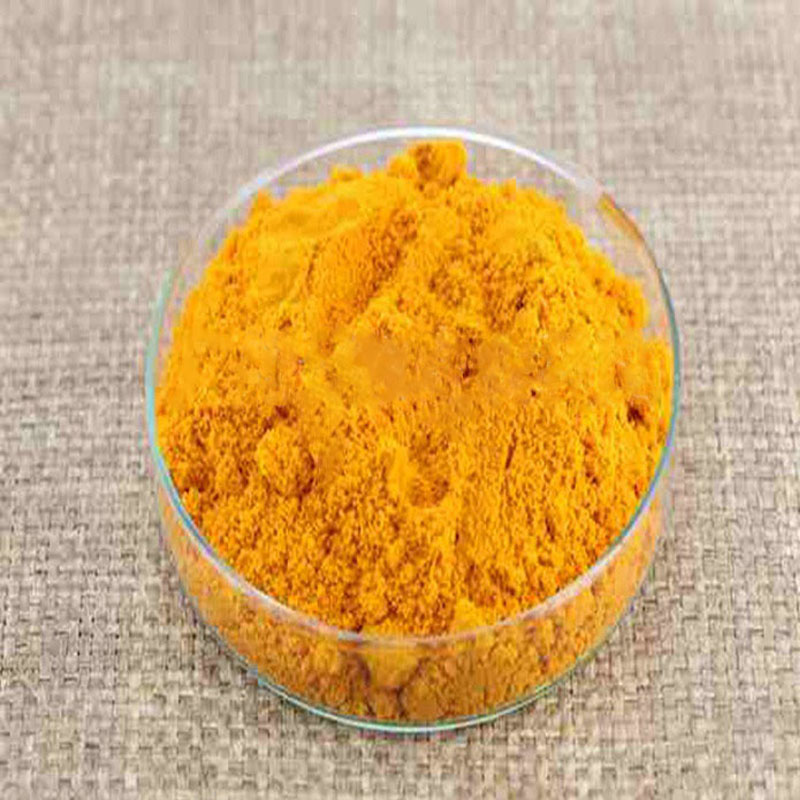
Turmeric, often referred to as “the golden spice,” has been a staple in various culinary traditions, particularly in South Asian cuisine. Its vibrant yellow hue and distinct flavor make it a favored ingredient in many dishes, but it’s not just its taste that captivates many; it's the impressive health benefits associated with curcumin, the primary active compound found in turmeric. This article delves into the significance of turmeric and curcumin powder, exploring their numerous health benefits, culinary uses, and considerations when incorporating them into our diets.
Understanding Turmeric and Curcumin
Turmeric (Curcuma longa) is a flowering plant belonging to the ginger family. The rhizome, or root, of the plant is harvested and often dried and ground into a fine powder. Curcumin, which makes up about 3-5% of turmeric's composition, is chiefly responsible for the spice’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. While turmeric has been utilized for thousands of years in traditional medicine practices like Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine, modern scientific research has begun to validate many of these time-honored claims.
Health Benefits
One of the most significant advantages of curcumin is its powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is often linked to a range of diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s. By incorporating turmeric and its curcumin content into our diets, we may help mitigate inflammation and potentially reduce the risk of these diseases.
Additionally, curcumin is a potent antioxidant, combating free radicals that cause oxidative stress in the body. This can lead to premature aging and contribute to various chronic conditions. Studies suggest that turmeric might play a role in enhancing the body’s own antioxidant defenses, further promoting overall health.
turmeric and curcumin powder

Research has also indicated that curcumin might aid in improving brain function. It’s believed to increase levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports neuron growth and development. Higher BDNF levels are linked to improved memory and cognitive function, making turmeric an excellent addition to a diet focused on brain health.
Culinary Uses
Beyond its medicinal benefits, turmeric is a versatile ingredient in the kitchen. It can be used in both savory and sweet dishes. The most popular usage is undoubtedly in curry powders, where it forms the base alongside other spices. However, turmeric can also be added to soups, rice dishes, smoothies, and even baked goods.
Turmeric lattes, also known as golden milk, have gained popularity as a comforting, anti-inflammatory beverage. Combining turmeric with milk (or plant-based alternatives), a touch of black pepper (which enhances curcumin absorption), and a sweetener creates a delicious drink that embodies the essence of wellness.
Considerations and Dosage
While turmeric and curcumin are generally considered safe for most people, it’s vital to consume them in reasonable amounts. Excessive intake can lead to digestive issues. For those looking to gain maximum health benefits, pairing turmeric with black pepper and healthy fats can significantly enhance curcumin absorption.
In conclusion, turmeric and curcumin powder are not just culinary delights; they hold a treasure trove of health benefits that can enhance our well-being. By integrating this golden spice into our diets, we can enjoy its unique flavors while capitalizing on its remarkable health-promoting properties. Whether it’s through a warm cup of turmeric tea or a savory curry, there are countless ways to embrace the power of turmeric in our daily lives.
-
Turmeric Rhizome Powder: A Golden Treasure from Roots to TableNewsJul.28,2025
-
The Versatile Application Of Crushed Red Hot Peppers: Lighting Up The Red Flames On The Dining TableNewsJul.28,2025
-
The Paprika: A Touch Of Vibrant Red In Color, Flavor, And CultureNewsJul.28,2025
-
Ground Turmeric: A Modern Examination of an Ancient SpiceNewsJul.28,2025
-
Capsicum Liquid Extract: Features, Applications, and ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
Application of Capsicum Liquid Extract in FoodNewsJul.28,2025